Claims about ‘safer supply’ diversion aren’t disinformation
This month, police in London, Ont., admitted to what critics have said all along: safer supply diversion is happening at alarming levels
By Sabrina Maddeaux
Last spring, Canada’s minister of mental health and addictions claimed critics’ concerns about “safer supply” diversion — the illegal selling and trading of taxpayer-funded addictive drugs — were based on lies.
“For Pierre Poilievre to state untrue information about safer supply, and try to create barriers to accessing harm reduction services that are saving lives amid this ongoing crisis, is incredibly irresponsible and dehumanizing to people who use drugs,” read a statement by then-minister Carolyn Bennett’s office.
Fast forward a year, and it’s clear which side was telling the truth.
This month, police in London, Ont., admitted to what critics said all along: diversion of pharmaceutically supplied opioids to the streets is happening at alarming levels. London is home to Canada’s longest-running safer supply program, which dates back to 2016 and was significantly expanded in 2020.
The London Police Service released data that shows a staggering 3,000 per cent increase in the seizure of hydromorphone tablets — the opioid predominantly given out by safer supply programs — over the last five years. In 2019, London police seized just under 1,000 tablets. By 2020, that number had tripled. In 2023, they seized 30,000 hydromorphone tablets.
For context, hydromorphone is as potent as heroin and just two or three of these pills, if snorted, can cause an overdose in an inexperienced opioid user.
Earlier this month, the city’s deputy police chief, Paul Bastien, told CBC’s London Morning, “We recognize the value that safe supply plays as part of that harm reduction piece, but diversion is an important issue that is affecting community safety. I won’t say that everyone’s doing it, but some of the tablets from safe supply are being diverted for that purpose.”
“Criminal groups are fairly adept at exploiting policy changes that are well intended. But unforeseen consequences sometimes arise and this appears to be, at least in part, one of them,” he continued.
A reasonable person may assume that, given this alarming new evidence, proponents of safer supply would change their tune about widespread diversion being “fake news.” Unfortunately, they haven’t.
Some activists are now claiming on social media that London’s spike in hydromorphone seizures was not caused by safer supply, but rather by a high-profile theft of 245,000 hydromorphone tablets from an Ontario pharmacy. Yet the spike in seizures began years before this theft and, according to multiple addiction physicians, the street price of hydromorphone collapsed in the city well before 2023, suggesting an earlier influx of diverted supply.
However, these mental contortions aren’t surprising. As more and more evidence of widespread diversion emerged over the past year, accusations of disinformation and misinformation haven’t stopped –– they have simply evolved. The narrative changed from “Diversion doesn’t exist” to “Fine, it exists, but only on a small scale” to, now, “Fine, diversion exists at scale, but imagine the alternative?”
This is the angle already emerging in British Columbia, where the province’s top doctor, Bonnie Henry, authored a damning report that acknowledges the regularity and harms of safer supply diversion, yet still concludes safer supply is “ethically defensible” and advocates for its expansion.
Like many safer supply activists, Henry often argues diversion isn’t a significant concern because most opioid deaths are caused by fentanyl.
While it’s true that most opioid deaths are attributable to fentanyl, hydromorphone is still incredibly dangerous. When diverted into the black market, it creates new addictions, often among young people, which culminate in fentanyl use.
Moreover, data indicate hydromorphone is implicated in an increasing share of drug-related deaths in young people in B.C. In 2019, there were no reported deaths involving hydromorphone. By 2022, that number jumped to 22 per cent. Similarly, a recent report by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health in Ontario found the number of youth in the province who self-reported using prescription opioids for “non-medical” reasons jumped 71 per cent between 2021 and 2023.
Still, safer supply activists continue to insist, despite overwhelming evidence to the contrary, that widespread diversion isn’t happening.
In 2017, Collins Dictionary declared “fake news” the word of the year. Since then, the term –– along with sister terms “misinformation” and “disinformation” –– have taken on a disturbing new life.
While fake news, misinformation and disinformation are very real democratic threats, some politicians and activists realized they could delegitimize opponents’ arguments and unflattering media stories by simply proclaiming them fake. Now, we’re in the dizzyingly ironic position of real news, and real facts, being dismissed as misinfo and disinfo by self-declared guardians of the truth.
This is the exact problem journalists and concerned medical professionals continue to face when raising the alarm on so-called “safer supply.” Despite the abundance of solid reporting, emerging data, whistleblower warnings and first-hand accounts of widespread diversion, harm reduction activists and their allies in government don’t just recklessly dismiss the problem, they weaponize the language of fake news to discredit a reality they don’t like.
Communities across Canada, and addicts themselves, deserve better.



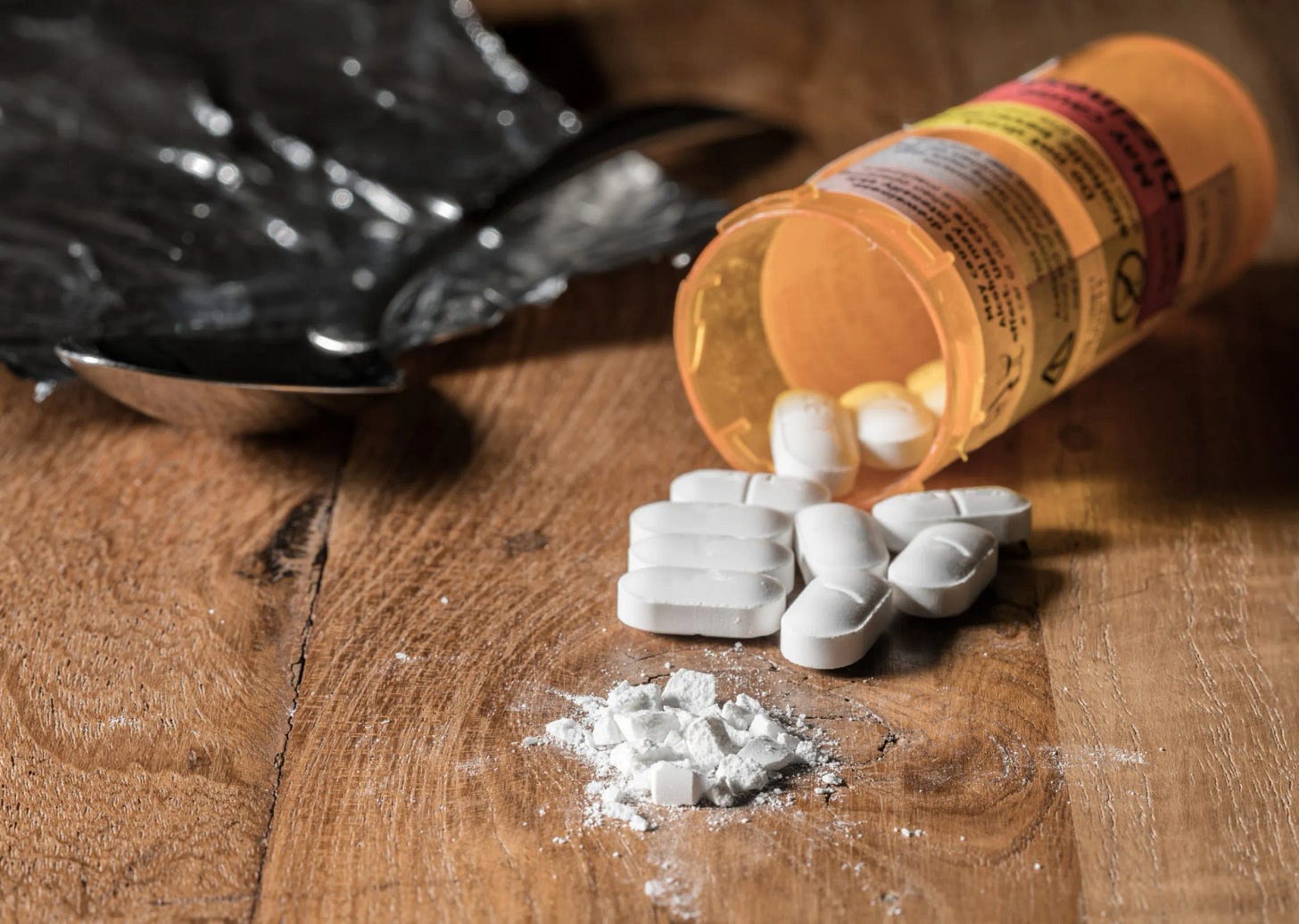

While new generations of addicts, our youth, are created through exposure to diverted supply, activists double down on their ideology and insulate their views with more manipulative language and assertions that are not demonstrably true.